De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Introduction
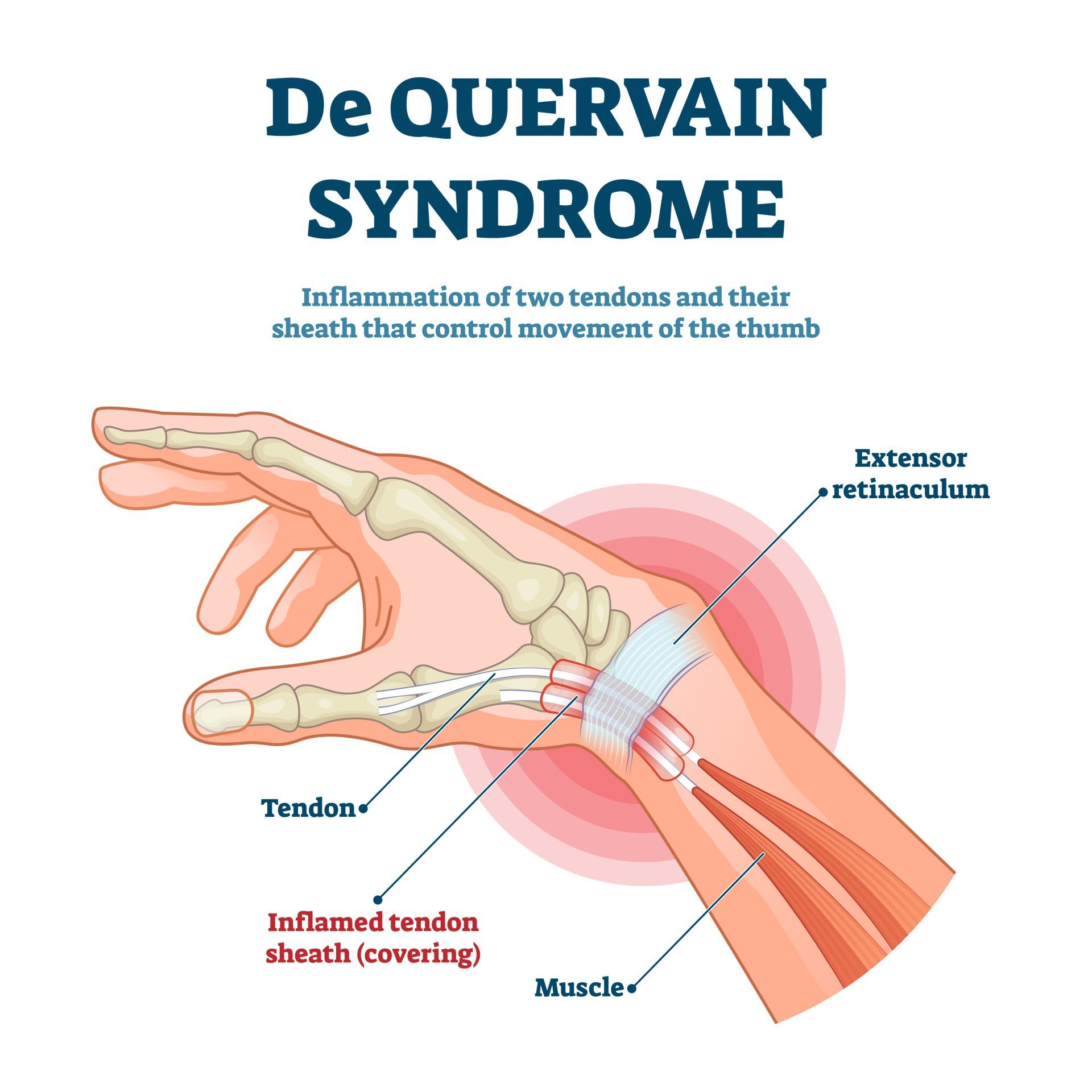
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis (also called De Quervain’s tendinosis) is a painful condition of two tendons at the level of the wrist on the side of the thumb
- It’s a repetitive strain injury due to overuse of two tendons used to move the thumb away from the other fingers
Anatomy
- Tendons are strong fibres of collagen that attach muscles to bones and therefore enable muscles to produce movement
- Tendons slide within a tissue that forms a tunnel called a sheath
- The sheath helps keep the tendons close to the bones
- Extensor tendons run on the back side of the wrist:
- Their function is to straighten the fingers and extend the wrist
- The extensor tendons are organised into 6 compartments at the level of the wrist
- The 1st compartment is on the side of the thumb and the 6th on the side of the little finger
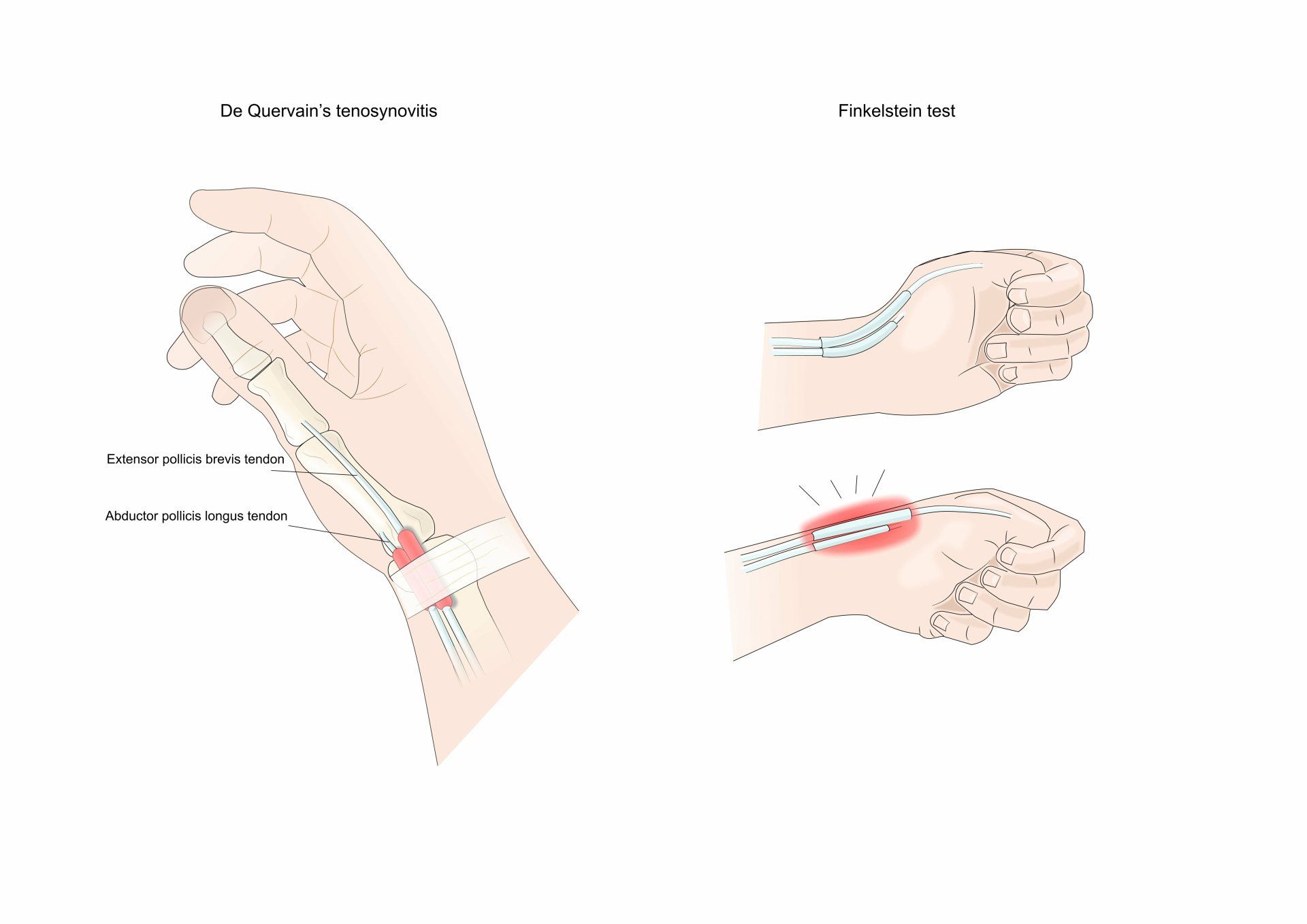
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis affects the 1st compartment which contains two tendons:
- Abductors pollicis longus:
- Its function is to tilt the wrist towards the thumb and abduct the thumb (moving the thumb vertically away from the palm)
- Extensor pollicis brevis:
- Its function is to tilt the wrist towards the thumb and extend the thumb (moving the thumb sideways away from the palm)
Pathophysiology
- It occurs due to thickening and/or swelling of the tendon or its covering sheath
- This causes friction and pain as the tendon struggles to slide through the sheath
How often does it occur?
- It is seen more commonly in patient who have tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow
- Often seen on both wrists in new mothers or those who look after children and resolves on its own once lifting the child is less frequent
Symptoms
- Pain occurs on the side of the wrist at the base of the thumb
- Pain is made worse when gripping
- The symptoms come on gradually
- Pain on moving the thumb especially when gripping objects
- Swelling at the base of the thumb has also been noted
Risk factors
- It is more common in women than men:
- Especially mothers of newborns who repeatedly lift the newborn with the thumbs away from the rest of the fingers
- Typically affects 30-50 year olds
- Most commonly affects the dominant wrist
- It is an overuse injury of the thumb particularly from repetitive grasping
- Can also be caused by a direct blow to the thumb or arthritis
- Provocative movement in particular is the sideways wrist motion whilst gripping such as:
- Lifting young children
- Gardening
- Racquet sports
- Skiing
- Using a hammer
- Long hours pressing playing computer games that involve pressing a button repeatedly with the thumb
Diagnosis
- The classic test for De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is the Finkelstein test
- The patient is asked to make a fist by wrapping their fingers over the thumb (as opposed to the more conventional thumb over fingers)
- Whilst keeping their fist in this position the doctor then moves the wrist sideways away from the thumb
- If this causes pain then it is a positive test for De Quervain’s tenosynovitis as the irritated tendons are forced down the narrowed overlying sheath
Treatment
- Most cases will settle with conservative management
- High rate of recurrence i.e. can come back once the symptoms settle
- First line treatment should be:
- Rest
- Avoiding repetitive thumb movements as much as possible
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Thumb immobilisation splint
- Ice
- Physiotherapy to strengthen muscles used to move the thumb
- Steroid injection into the affected tendon compartment of the wrist to help reduce
- Studies have shown that 20% of patients using thumb immobilisation splint alone for 6 weeks had improvement in symptoms and this increased to 60% when combined with anti-inflammatory medications
- The splint should allow some movement of the thumb as opposed to completely immobilising it
- Surgical treatment is considered for cases when conservative management has failed:
- It has a high success rate
- A small cut is made on the wrist over the painful side and the sheath is released over the irritated tendons
- This removes the pressure on the tendons and allows them to heal
- The operation can be performed under local or regional anaesthesia
- There is a nerve (superficial radial nerve) around the surgical incision site which provides sensation to the area so it is important to avoid this potential complication
Prevention
- Avoiding provocative movements that cause pain
- Taking breaks when having to carry out a repeated wrist motion
- Keeping your hand and forearm muscles strong
Further helpful information can be found here on:

Introduction Cubital Tunnel Syndrome occurs when the ulnar nerve is compressed within a tunnel on the inner (medial) side of the elbow just behind the bony prominence of the inner aspect of the elbow called the medial epicondyle Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is the second most common cause of peripheral nerve compression: The most common one being carpal tunnel syndrome (compression of the median nerve at the wrist) The ulnar nerve is one of the three main nerves of the upper limb: The other two nerves of the upper limb are the median nerve and the radial nerve The ulnar nerve travels from the neck past the elbow and wrist and into the hand: Along the way it travels past some narrow areas where it can be constricted and cause symptoms for the patient The most common site of ulnar nerve compression is in the cubital tunnel at the elbow The second most common site is in Guyon’s canal in the hand When someone accidentally hits the inner side of the elbow (often termed hitting the funny bone) they get a sharp tingling sensation on the inner side of the elbow and forearm: This occurs because the ulnar nerve was hit at the site of the cubital tunnel where the nerve is close to the skin surface and therefore easily injured from outside forces
Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that causes numbness, tingling and weakness in the hand specifically affecting the thumb, index and middle fingers: The little and ring fingers are not affected as they are supplied by another nerve called the ulnar nerve It is the commonest cause of peripheral nerve entrapment It is caused by compression of the median nerve as it passes from the forearm into the hand through a passage called carpal (i.e. wrist) tunnel The median nerve is one of three main nerves that supply the upper limb: The other two nerves are the ulnar nerve and the radial nerve

Introduction Tennis elbow (also known as lateral epicondylitis) is an overuse injury of the forearm tendons that originate over the lateral epicondyle of the humerus (bony prominence on the outside of the elbow) and act to bring the wrist backward away from the palm Whilst tennis players are particular prone to this condition it does not occur exclusively to them

Introduction This term is also known as repetitive motion or stress injury and occurs as a result of carrying out the same motion repeatedly over time causing injury to muscles and tendons It is associated with repetitive tasks, sustained or awkward position, forceful exertion, vibration or compressive forces It can affect almost any joint in the body Most commonly affected areas are hands, wrists, shoulders and neck It is thought to affect 5-10% of the general population but can be as high as 20-40% in specific working populations