Bursitis
What is a bursa?
- A bursa is a small fluid filled sac that is located over pressure points between a bony prominence and the overlying skin, tendon or muscle
What is the function of a bursa?
- The function of a bursa is to reduce the friction between the bony prominence and the overlying structure
What is knee bursitis?
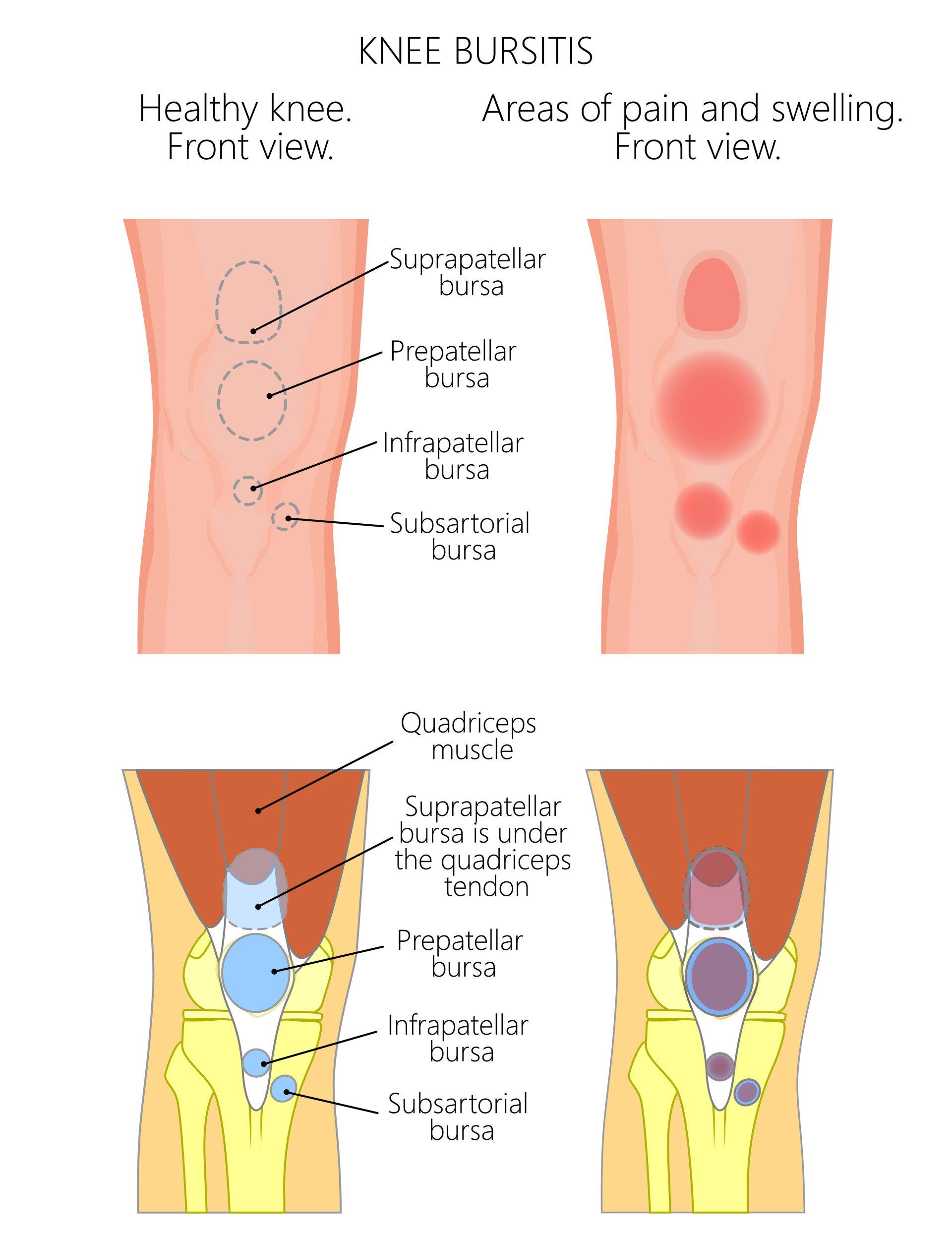
- Knee bursitis is inflammation of any of the numerous bursae located around the knee joint
- There are approximately 13 bursae around the knee and any of them can become inflamed and cause pain
What are the most common locations for knee bursitis?
- The four most common bursa that get inflamed are:
- Suprapatellar:
- Located proximal to the patella
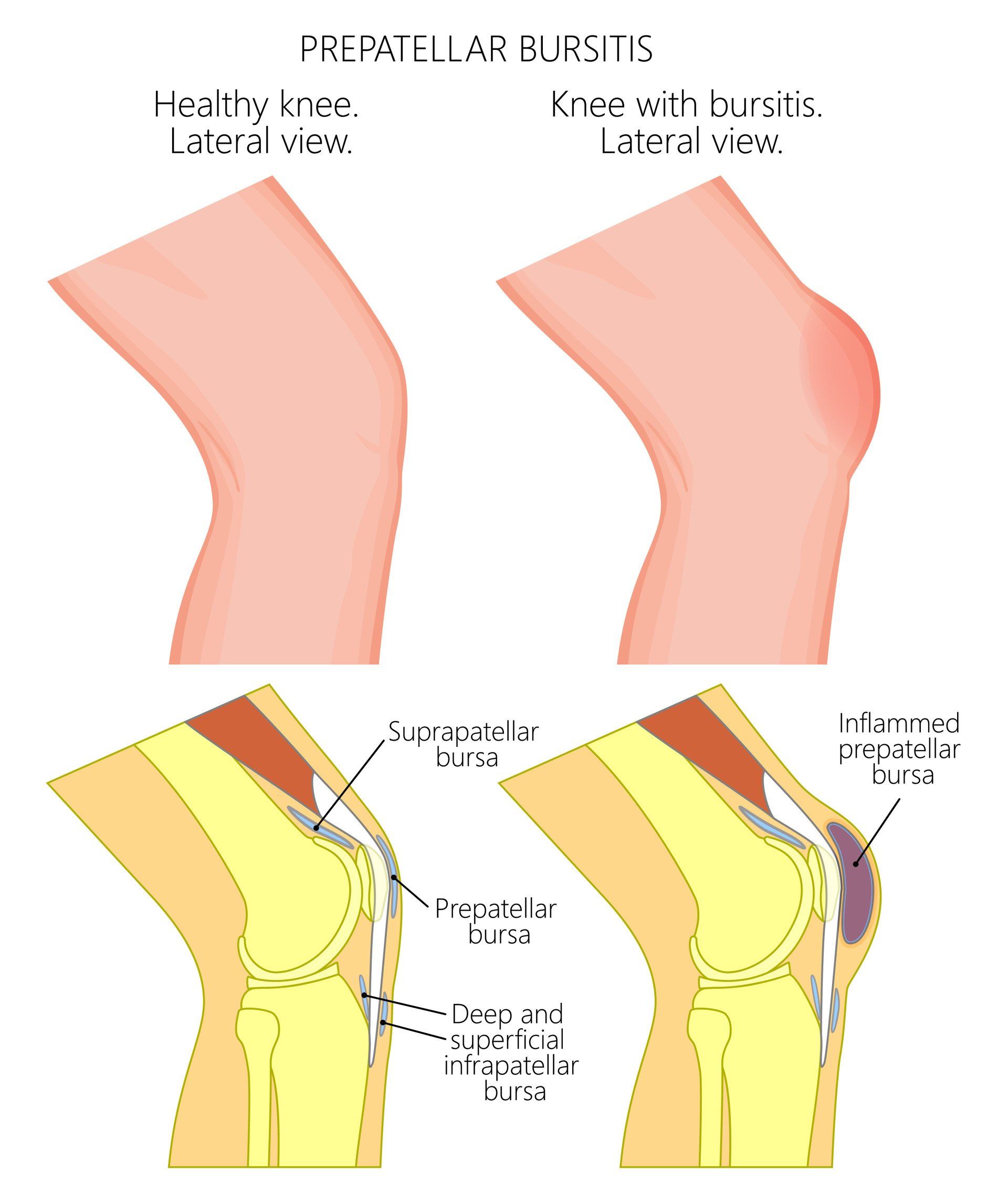
- Prepatellar:
- Located over the patella
- Infrapatellar:
- Located distal to the patella
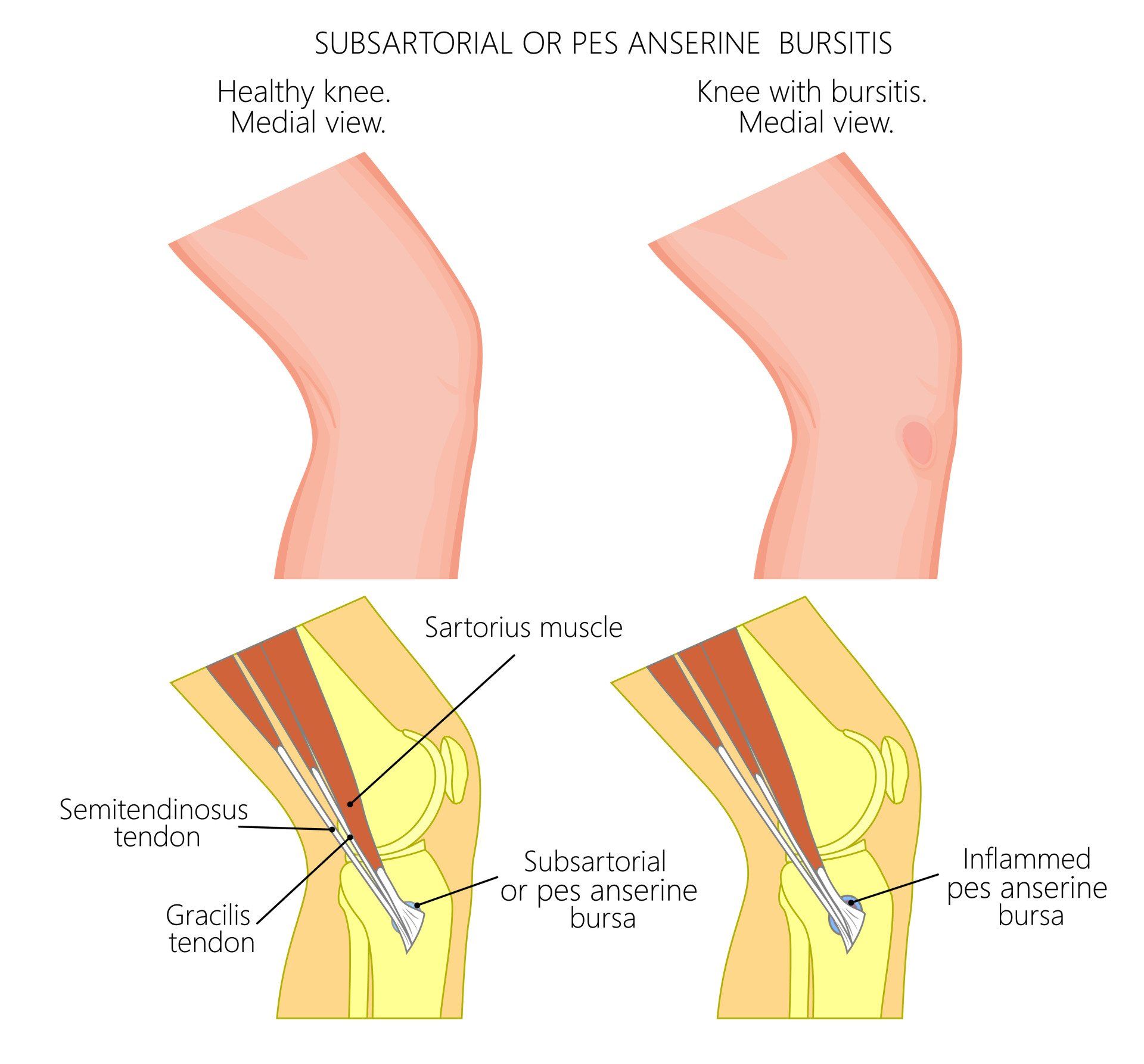
- Pes Anserine:
- Locatedover the pes ansirinus (proximal medial aspect of the tibia anteriorly)
What is the cause of bursitis?
- Bursitis at the front of the knee commonly occur from repetitive frictional forces and pressure on a bursa at the front of the knee such as those who kneel a lot e.g. carpenters, plumbers, tilers
- Bursitis at the back of the knee (also known as Baker’s cyst) occurs from fluid accumulation secondary to an injury or arthritis inside the knee
- Infection of the bursa
- Excessive activity
- Conditions that increase fluid inside the knee joint such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and gout
Symptoms
- Symptoms vary depending on:
- location of the affected bursa
- cause of the bursitis
- Swelling
- Pain especially when pressure is applied over the bursa
- Warmth
Investigations
- Blood tests:
- Help to differentiate inflammation from infection
- X-rays:
- Help identify arthritis or other bone pathology
- MRI scan:
- Helps to delineate soft tissue structures better than Xrays
- Will show dimensions of the bursa and pathology inside the knee which could contribute to the formation of bursitis
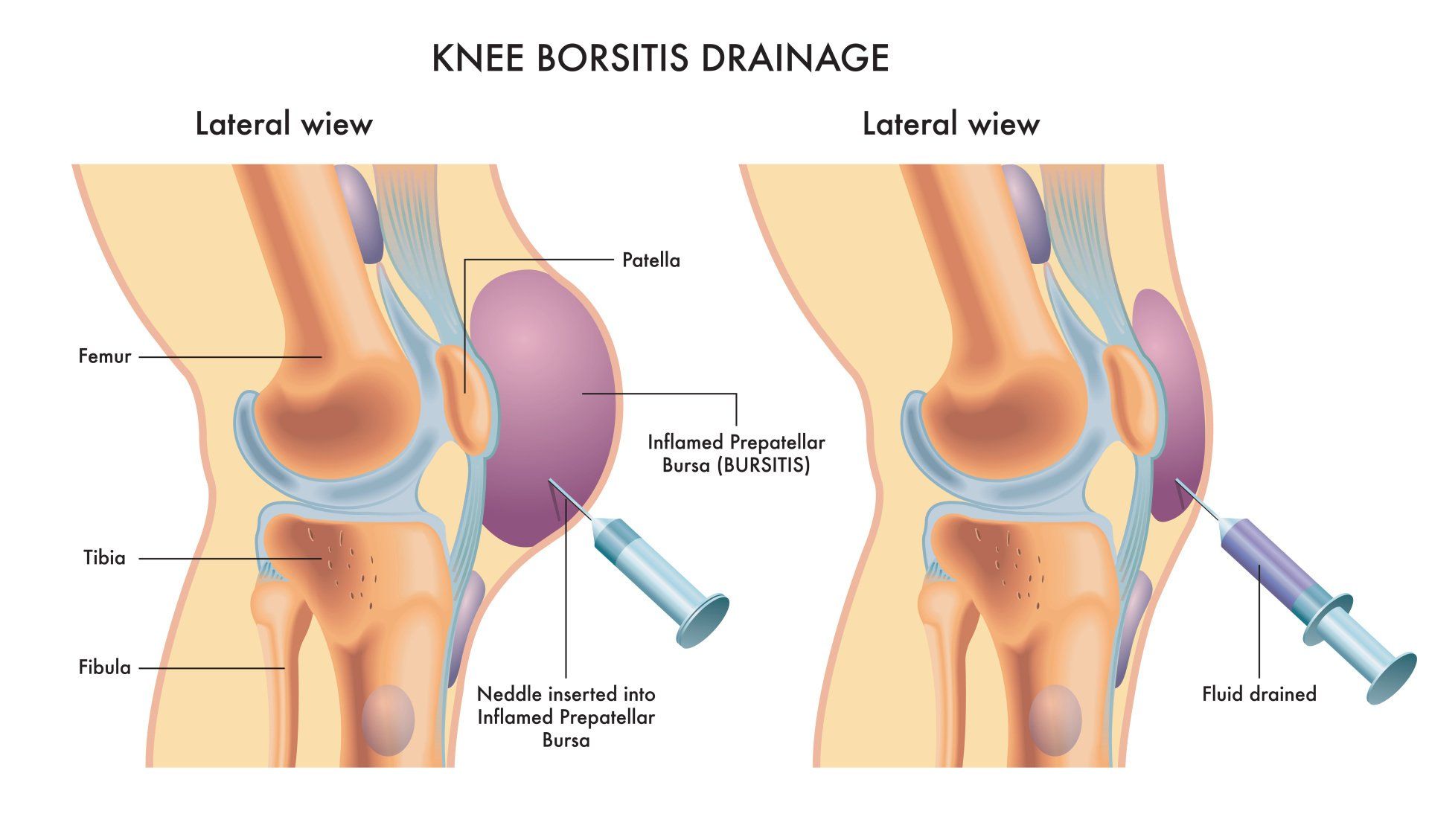
- Aspiration of the fluid:
- This involves sticking a needle in the bursa and collect some fluid to send it to the lab to investigate its contents and exclude infection
- It will also help with pain relief
What are the treatment options for bursitis?
- Conservative:
- Conservative management is usually all that is indicated:
- Avoiding friction over the area is key
- Paracetamol
- Anti-inflammatories:
- They help to reduce inflammation and swelling in the knee
- Rest:
- This helps to reduce strain on the knee and subsequent swelling
- Ice:
- Frequent icing of the knee helps to reduce inflammation and swelling inside the knee
- Compression with an elastic bandage:
- Wrapping the knee up with an elastic bandage will help reduce knee swelling
- Elevation:
- Elevating the leg will help reduce knee swelling with the help of gravity
- Aspiration of the bursa will help reduce swelling and pain but has a high chance of recurrence
- If the bursa is infected need either intravenous or oral antibiotics pending on severity
- Operative:
- Rarely indicated:
- Fluid can reaccumulate so unnecessary exposure to an operation
- Operative scar has poor history of healing and can cause a chronic discharging sinus
- A sinus is a tract that forms between skin and bursa and fluid keeps coming out which then increases the risk of the bursa becoming infected
- Consider washout and debridement in resistant cases of infected bursitis
Prevention
- Wear kneepads especially for those who knee a lot (e.g. plumbers, carpenters, bricklayers) as they reduce pressure and friction at the front of the knee
- Take regular breaks if have to kneel
- Avoid keeping your knees too flexed
- Apply ice to knee after period of excessive kneeling and knee squatting
- Lose weight so as to offload forces in an arthritic knee