Lower Limb Malalignment
What is lower limb malalignment?
- Limb malalignment means that there is a deformity in the limb when looking at it from:
- The front
- The side
- Above (axial rotation also called torsion)
- Limb length discrepancy (the lower limbs are not of equal length)
- Or combination of the above
Why is it important for the lower limbs to be correctly aligned?
- For the knee to function well and remain healthy it needs to be properly aligned so that the stresses around the knee are balanced
- When there is lower limb malalignment the stresses are transferred more towards one side of the knee which is detrimental to function and symptoms
- Much like the wheels on a car, if they are not balanced and correctly aligned one side is more rapidly worn out and the car doesn’t drive as well, the same happens to the knees in lower limb malalignment:
- However good the tyres are if the wheels are not properly aligned and balanced the stresses will concentrate on one side and therefore cause early wear and tear
What are the consequences of lower limb malalignment?
- When limb malalignment is present, it shifts the forces to one side of the knee joint which has numerous consequences such as:
- The side of the knee joint that is exposed to increased forces is worn out quicker (earlier arthritis) and becomes painful
- Ligaments can become stretched on one side and contracted on the other
- Adversely affect muscle function which then has consequences on knee motion and stability
- It can have knock on effect on other joints of the lower limb and the lower back which can become symptomatic
What are the causes of limb malalignment?
- Developmental:
- Some patients are born with a malalignment
- Trauma:
- A malalignment can occur secondary to trauma to a long bone of the limb such as the tibia or femur if it doesn’t set correctly
- A fracture involving the knee joint surface can lead to an angular deformity of the lower limb and rapid onset of arthritis if they do not heal in an optimal position
- Degenerative:
- Wear and tear to one side of a joint will narrow down that compartment causing a limb deformity
Mechanical explanation of limb deformity
- A line drawn from the centre of the hip to the centre of the ankle should cross the middle of the knee:
- This is called the mechanical axis of the lower limb and shows where the forces act on the knee when standing
- In such a scenario the forces are equally distributed in the knee
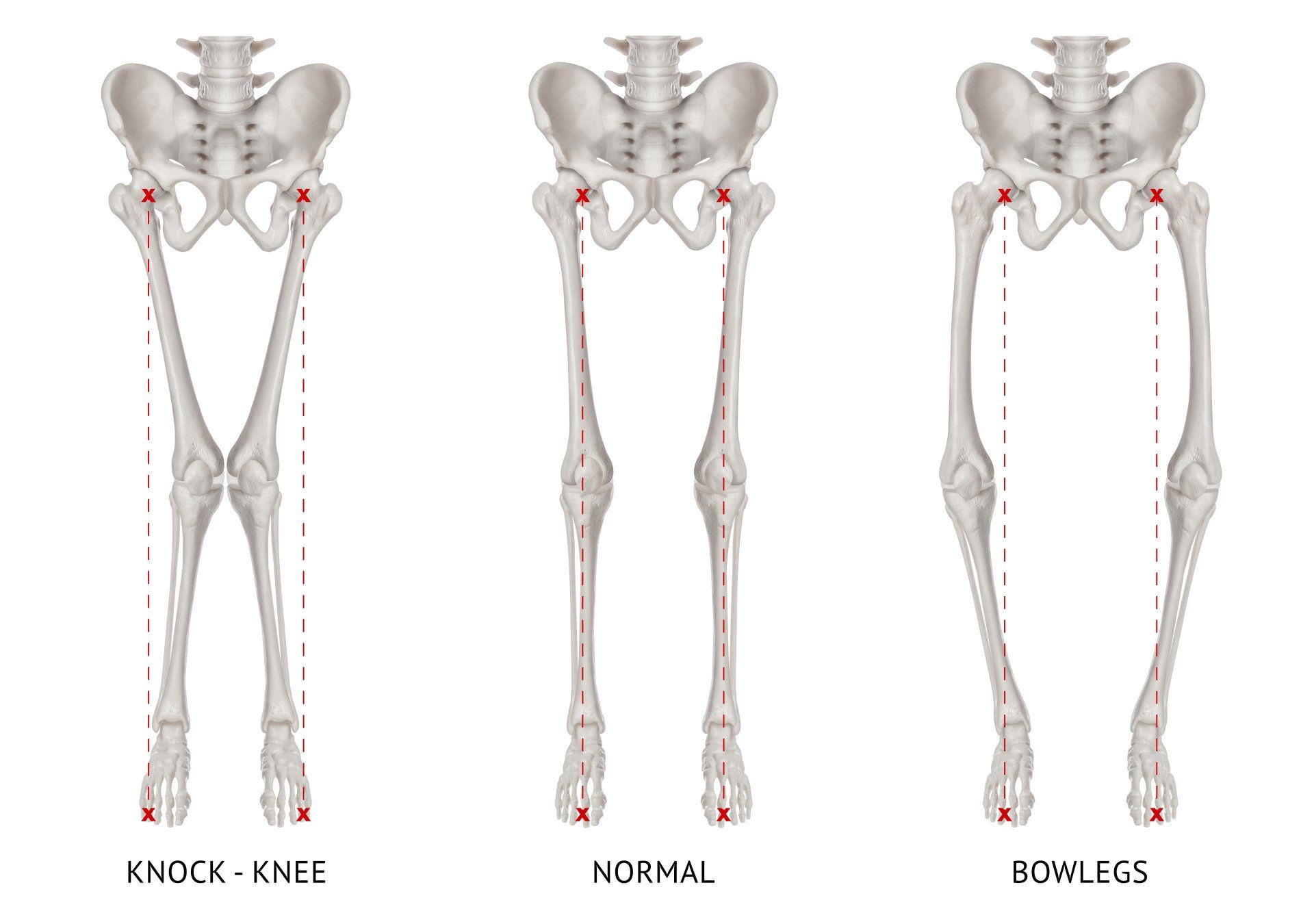
What is varus knee deformity?
- When the mechanical axis passes on the medial (inner side) as opposed to the middle of the knee it is because the ankle lies closer to the midline than the knee:
- This is called varus (bow legged) deformity of the knee
- As a result, most of the forces go through the medial (inner) side of the knee, leading to earlier damage of the meniscus and articular cartilage which leads to medial compartment osteoarthritis
- It is the commonest type of deformity around the knee
What is valgus knee deformity?
- When the mechanical axis falls lateral (outer side) to the middle of the knee it is because the ankle lies further away from the midline than the knee:
- This is called valgus (knock kneed) deformity of the knee
- As a result, most of the forces go through the lateral (outer) side of the knee, leading to earlier damage of the meniscus and articular cartilage which leads to lateral compartment osteoarthritis
- It is less common than varus knee deformity
Lower limb alignment changes as the child grows
- It is normal for newborns and children to go through changes in their lower limb alignments as they grow
- A new born has moderate varus knees
- At around 18 months the lower limbs are straight
- By 2.5 years the knees become valgus
- Around 4-6 years the lower limbs start to take their definitive alignment seen in adults
Are both legs affected?
- Lower limb malalignment can affect one side or both
- It can affect one side more than the other
- On rare occasions, one knee has a varus deformity and the other knee a valgus deformity:
- This is termed windswept deformity as the knees point towards one side of the body
Symptoms of limb malalignment
- If mild it can be asymptomatic
- As it becomes more severe, it presents with arthritic symptoms on one side of the knee:
- Pain on the affected side of the knee
- Stiffness and swelling
- Grinding, clicking or catching of the knee
Can I prevent a limb malalignment?
- As with knee arthritis keeping fit, healthy and slim helps preserve the lower limb joints
- When lower limb malalignment is more severe treating it early is easier than leaving it to deteriorate as the arthritis will spread to the other side of the knee and the knee ligaments can be permanently stretched on one side and contracted on the other side making surgery more complex
- If there is a traumatic injury to the knee joint surface, they should be treated promptly and effectively:
- If the joint surface caves in from the injury it can lead to malalignment
What is the purpose of an osteotomy?
- To shift the forces away from the painful side and relieve symptoms
- Delay the onset of arthritis
- Rebalance the forces on the knee joint and consequently on the ligaments as well
- Will also reduce adverse impact on the joints above and below the knee
Osteotomy and biological knee preservation
What is the benefit of osteotomy versus a knee replacement?
- The benefit of an osteotomy versus a knee replacement is that is preserves the patient’s own knee and there is greater bone stock for when a knee replacement will eventually be carried out
- Whilst a partial knee replacement may also be suitable for some patients, for the younger patients with malalignment an osteotomy would be a better option
- Essentially an osteotomy delays the need for knee arthroplasty
What is biological knee preservation and what are the benefits?
- Biological knee preservation encompasses a multitude of treatment options (of which osteotomy is one of them) that aim to preserve the patient’s native structures and delay the need for a joint replacement
- Once a joint replacement is carried out then once they are worn out or loosen with time then they may require revision joint replacement surgery
- Each time a revision joint replacement is carried out bone stock is lost and bigger implants are required
- After two revision joint replacements the treatment options are running out
- Hence the need to delay a joint replacement as much as possible in younger patients (<60 years)
What do the treatment options for lower limb malalignment depend on?
- The treatment options depend on:
- The age of the patient
- Their symptoms
- The cause of the malalignment
- The rate of progression of the deformity
- The patient’s expectations
- The patient's overall physical health
What are the conservative treatment options for lower limb malalignment?
- Strengthening of muscles in the lower limb and core
- Weight loss
- Shoe modifications and insoles
- Wearing a corrective brace:
- This is a special knee brace that a applies a force to the knee to help correct the malalignment
- Whilst this avoids an operation it can be cumbersome to wear long term
- It helps confirm that a corrective osteotomy would improve the patient’s symptoms
What is the purpose of an osteotomy ?
- The purpose of an osteotomy is to realign the lower limb so that the forces are shifted away from the damaged painful side and as a consequence:
- Relieve pain
- Prolong the natural joint surface
- Avoid the need for an early joint replacement
What are the various osteotomy options around the knee to correct lower limb malalignment?
- High Tibial Osteotomy:
- This involves cutting the tibia (shin bone) close to the knee but not affecting the knee joint surface
- Realigning the tibia and holding it in place with metalwork
- Further information can be found
here
- Distal Femoral Osteotomy:
- This involves cutting the femur (thigh bone) close to the knee but not affecting the knee joint surface
- Realigning the femur and holding it in place with metalwork
- Further information can be found
here
- Derotational osteotomy:
- This involves cutting the long bone, rotating its axis of the upper segment in relation to the lower segment and fixing it in place with metalwork
- Placing an external fixator frame:
- This involves a frame outside of the limb that is connected to the bone via numerous wires
- Examples include Ilizarov or Taylor Spatial frame
Further information on knee realignment osteotomies can be found here.