Meniscal Cyst
What is a meniscal cyst?
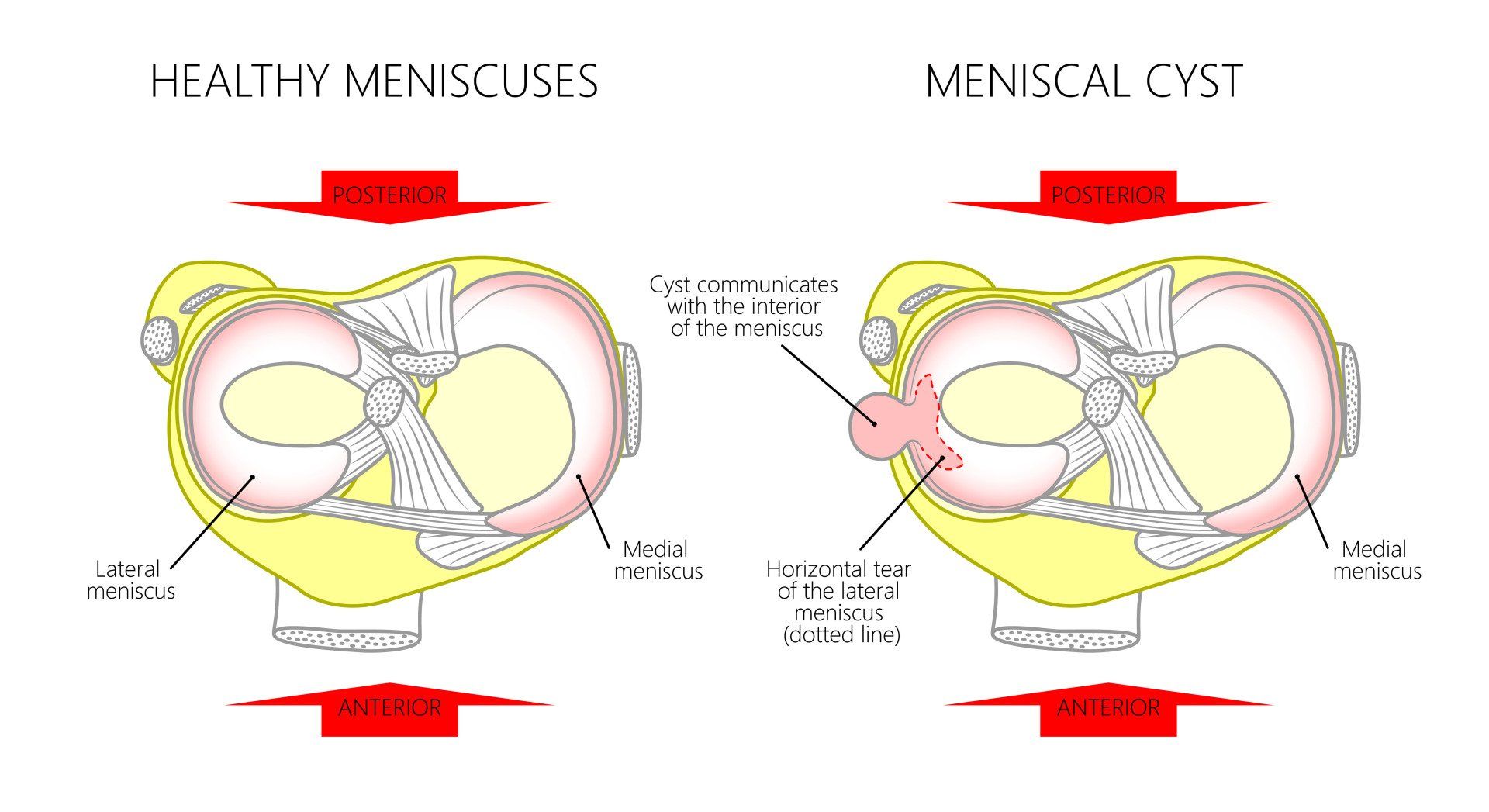
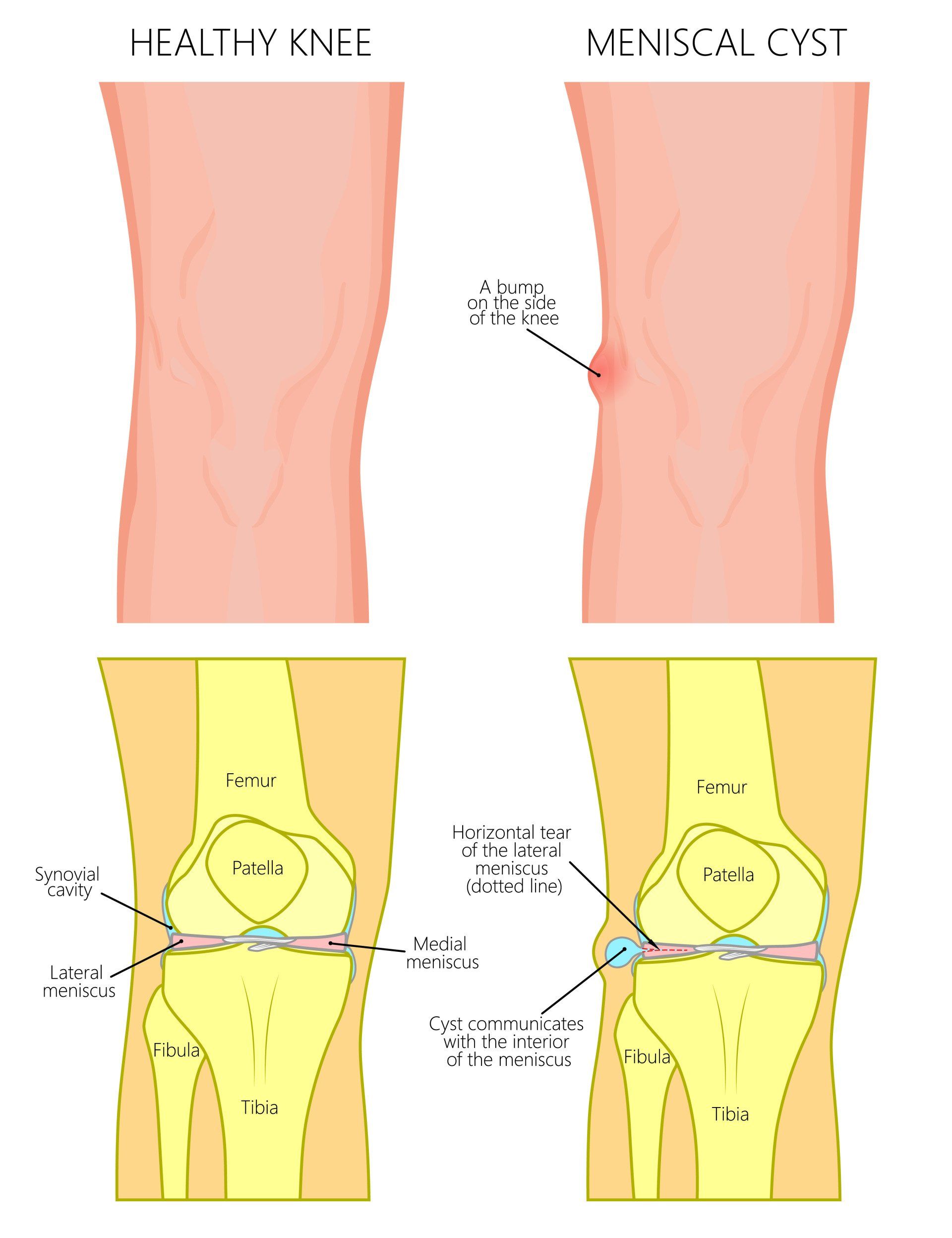
- A meniscal cyst is a localised collection of synovial fluid within or adjacent to the meniscus most commonly as a result of a meniscal tear
What types of meniscal cysts are there?
- There are two types of meniscal cysts:
- Perimeniscal cysts:
- located within the meniscus
- Parameniscal cysts:
- Located beyond the margins of the meniscus
- Baker’s cyst is an example of one
Aetiology
- Perimeniscal cysts (which are considered here) are often associated with a meniscal tear typically a degenerative tear
- The meniscal tear is thought to create a one-way valve mechanism:
- Synovial fluid from the knee joint goes through the meniscal tear and into the cyst but cannot go back into the joint
- However not all meniscal cysts are associated with a meniscal tear
What are the risk factors for meniscal cysts?
- Risk factors are:
- Twisting knee injury causing a meniscal tear
- Previous knee injury such as ligament injury
- Age, as this increases the chance of a degenerate meniscal tear
What are the most common locations for meniscal cysts?
- 90% of meniscal cysts are located in the lateral meniscus:
- Lateral meniscal cysts are usually anterior (front)
- 10% of meniscal cysts are located in the medial meniscus:
- Medial meniscal cysts are usually posterior (back)
How frequent are meniscal cysts?
- Meniscal cysts are thought to occur in around 5% of the general population
- They are found in ~2% of MRI scans
Symptoms
- Pain on the side of the knee joint line:
- Especially when standing on the affected leg
- Clicking
- 40-60% of cysts are palpable
- Knee swelling
- Can be completely asymptomatic
Investigations
- MRI scan is the gold standard:
- Helps to identify size and location of cyst as well as any associated meniscal tear
- Ultrasound scans can also be helpful
Conservative treatment options for meniscal cyst
- Anti-inflammatories:
- They help to reduce inflammation and swelling in the knee
- Rest:
- This helps to reduce strain on the knee and subsequent swelling
- Ice:
- Frequent icing of the knee helps to reduce inflammation and swelling inside the knee
- Compression with an elastic bandage:
- Wrapping the knee up with an elastic bandage will help reduce knee swelling
- Elevation:
- Elevating the leg will help reduce knee swelling with the help of gravity
- Ultrasound guided needle aspiration of cyst and injection of steroid:
- Avoids risks of surgery
- High risk of recurrence
Surgical treatment options for meniscal cyst
- Knee arthroscopy and debridement of meniscal tear:
- Aim is to disrupt one-way mechanism and allow free passage of synovial fluid in both directions
- 90% of patients report good to excellent results
- If the cyst is large or not communicating with meniscal tear, can be surgically removed from the outside
- Meniscal tear where possible can be repaired with meniscal sutures to seal off the valve